How to implement Linked List using Dictionary in Python
Implementation of Linked List data structure with it's function using Dictionary data type in Python.
Table of contents
Introduction
In this blog, we will implement Linked List data structure using in-built data type dictionary in Python.
This blog gives you an idea about abstract data structure and gives a different way to implement linked list in Python.
Linked List : Instead of continuous memory allocation for data (like an array) we use linked list data structure to store data in non-continuous memory location by connecting them using Node. Linked List size can be changed unlike an array. Linked List is an abstract data type.
Dictionary : A dictionary is used to store key-value pairs. Represented by { }.
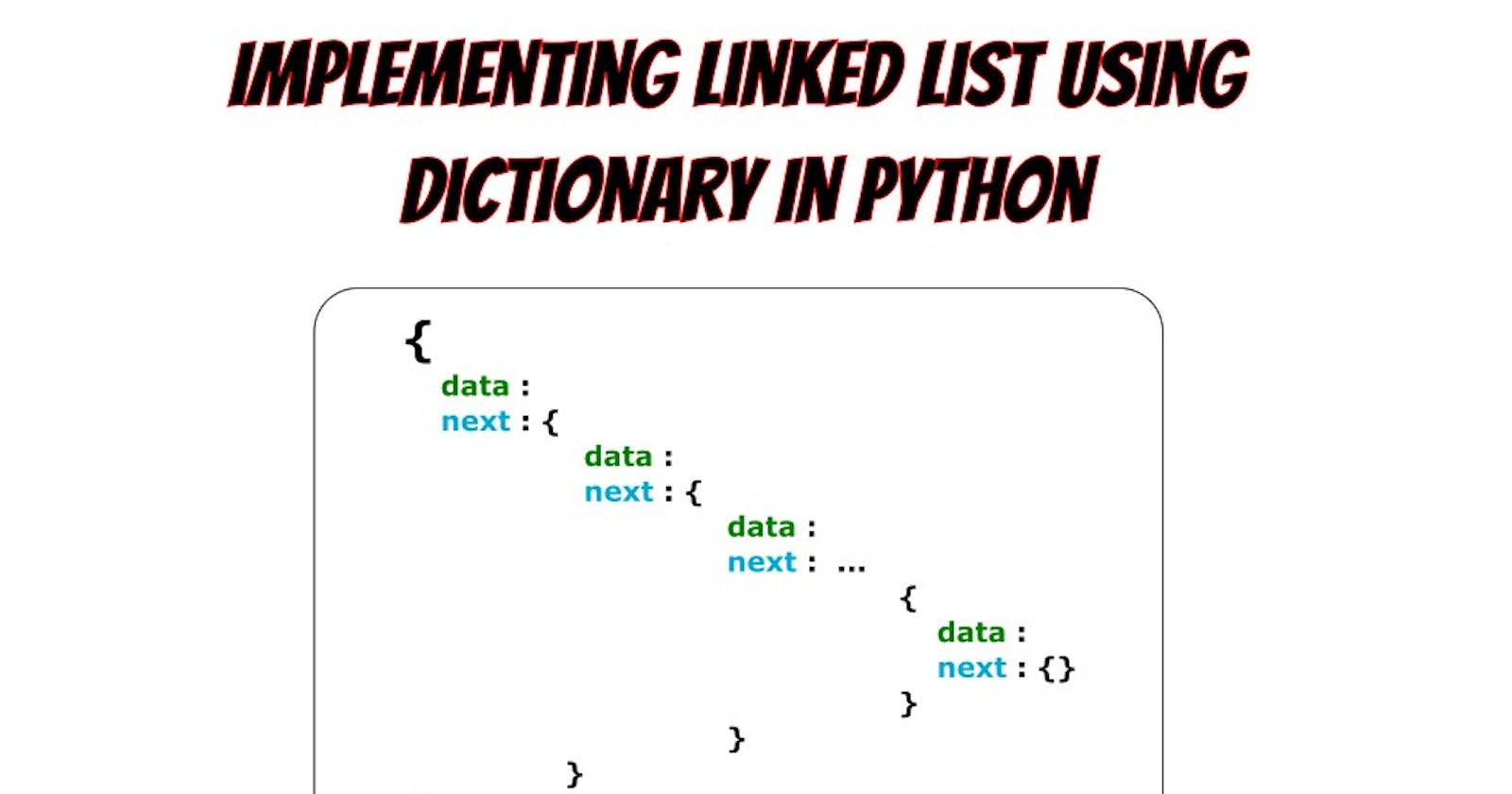
How to Linked List implemented using Dictionary looks like?
items = {
"data" : "Coke",
"next" : {
"data" : "Cheese",
"next" : {
"data" : "Biscuits",
"next" : {
"data" : "Soap",
"next" : {}
}
}
}
}
In the above example, there are two key-value pairs in the dictionary, one is storing data and the other is pointing to the next node which is also a dictionary.
"Coke" -> "Cheese" -> "Biscuits" -> "Soap" -> None
Here, next : {} means linked list ends.
Traversal in Linked List
Code :
#Temporary variable used for traversal
traversalVariable=items
#Looping through this temporary variable
while traversalVariable != {}:
print(traversalVariable["data"])
traversalVariable=traversalVariable["next"]
If items={} means an empty linked list.
In first iteration, traversalVariable={"data" : "Coke", "next" : {...}} to traversalVariable={"data" : "Cheese", "next" : {...}}
Inserting at the End of Linked List
To add node at end of linked list we will traverse till traversalVariable["next"]!={}. Then, traversalVariable["next"] = new_node.
We will also check the condition that the linked list is not empty in starting of the function.
Code :
def insertEnd(head,value):
#If linked list is empty
if head=={}:
head["data"]=value
head["next"]={}
return
#New node we want to add it our linked list
new_node={"data" : value, "next" : {}}
#We will traverse till traversalVariable["next"]!={}
traversalVariable=head
while traversalVariable["next"]!={}:
traversalVariable=traversalVariable["next"]
traversalVariable["next"]=new_node
return
Insert at the Beginning of the Linked List
We simply can't add node at beginning at the Linked List, we have to use a trick to do so, Code :
def insertBegin(head,value):
#If linked list is empty
if head=={}:
head["data"]=value
head["next"]={}
return
#New node at beginning
new_node={}
new_node["data"]=head["data"]
new_node["next"]=head["next"]
head["next"]=new_node
head["data"]=value
return
This is how it looks :

Insert After a given Position
We will traverse till key is found in Linked List and insert node after that. If key not found then we print error and exit the function.
Code :
def insertAfter(head,key,value):
#If Linked List is empty.
if head=={}:
print("Linked List is Empty, Key not found.")
return
#Traverse till key not found.
traversalVariable=head
while traversalVariable!={} and traversalVariable["data"]!=key:
traversalVariable=traversalVariable["next"]
#If Key not found in Linked List.
if traversalVariable=={}:
print("Key not found.")
return
#If Key found.
new_node={}
new_node["data"]=value
new_node["next"]=traversalVariable["next"]
traversalVariable["next"]=new_node
return
Deletion at Beginning
In this, we will return the head pointer of the linked list after deletion.
Code :
def deleteBegin(head):
#If linked list is empty
if head=={}:
print("Linked List is empty.")
return {}
#Move the head pointer to next node
head=head["next"]
return head
We can also do it without returning the head pointer (similar to insert at beginning).
Delete at Intermediate Position
Here we are not deleting at beginning. So, here we don't need to return the head pointer.
Here in while loop, we check two conditions:
We are not at the last node.
We did not found the key.
Code :
def deleteIntermediate(head,key):
#If linked list is empty
if head=={}:
print("Linked List is empty.")
return
#Traverse till key not found
traversalVariable=head
while traversalVariable["next"]!={} and traversalVariable["next"]["data"]!=key:
traversalVariable=traversalVariable["next"]
#If key not found
if traversalVariable["next"]=={}:
print("Key not found. No deletion happened.")
return
#If key found
else:
traversalVariable["next"]=traversalVariable["next"]["next"]
return
Remember this function does not works for key at beginning of linked list.
Some things to check your knowledge
Make Search Function
Make a function to replace data
Implementing using Class and make its method(of linked list).
Code of 3rd :
class LinkedList:
def __init__(self):
self.head={}
def insertBegin(self,value):
if self.head=={}:
self.head["data"]=value
self.head["next"]={}
else:
new_node={}
new_node["data"]=value
new_node["next"]=self.head
self.head=new_node
def insertEnd(self,value):
if self.head=={}:
self.head["data"]=value
self.head["next"]={}
return
traversalVariable=self.head
while traversalVariable["next"]!={}:
traversalVariable=traversalVariable["next"]
traversalVariable["next"]["data"]=value
traversalVariable["next"]["next"]={}
def insertAfter(self,key,value):
traversalVariable=self.head
while traversalVariable and traversalVariable["data"]!=key:
traversalVariable=traversalVariable["next"]
if traversalVariable=={}:
print("Key not found. No insertion.")
return
else:
new_node={}
new_node["data"]=value
new_node["next"]=traversalVariable["next"]
traversalVariable["next"]=new_node
return
def printList(self):
traversalVariable=self.head
while traversalVariable:
print(traversalVariable["data"])
traversalVariable=traversalVariable["next"]
def deleteBegin(self):
if self.head=={}:
print("Linked List is Empty.")
return
self.head=self.head["next"]
def deleteIntermediate(self,key):
if self.head=={}:
print("Linked List is Empty.")
return
if self.head["data"]==key:
self.head=self.head["next"]
return
else:
traversalVariable=self.head
while traversalVariable["next"]!={} and traversalVariable["next"]["data"]!=key:
traversalVariable=traversalVariable["next"]
if traversalVariable["next"]=={}:
print("Key not found. No deletion happened.")
return
else:
traversalVariable["next"]=traversalVariable["next"]["next"]
return
#Sample Test Case
l=LinkedList()
l.insertBegin(1)
l.insertBegin(2)
l.insertBegin(3)
l.insertAfter(2,10)
l.deleteIntermediate(4)
l.printList()
Source
Dr Madhavan Mukund Sir's video : https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=mfLHZBHNezk